Camera Selection
With a large amount of interest in the sUAS community focused on the uses in the agriculture industry, we have begun development on a lightweight, imaging set for acquiring NIR and RGB (visible spectrum) data sets. the "Horizon 1080 p HD camera" from Foxtech seems to be a good candidate. Our goal will be to modify one camera by removing the low pass or infrared blocking filter from behind the lens set and replacing with an "ultrablue" filter. The other camera we will leave as is. This camera system has been designed specifically for use with small remotely piloted aircraft and will produce images similar in quality to the GoPro camera. This design also features the ability of triggering the shutter via an extra channel on the remote or directly from the APM's (autopilot) trigger output. This will allow us to remove the servo from the system thereby decreasing the overall weight and increasing reliability through simplifying the electrical-mechanical interface.
After removing the infrared blocking filter from the back of the lens a small peice of #74 "Ultra-blue" filter was cut to fit into the back of the lens holder. This filter has been developed by Public Labs to work best with CMOS sensors when capturing NIR images for vegetation analysis
CMOS image sensor capable of seeing in the near infrared range once the filter is removed
The camera lens disassembled to remove infrared blocking filter
The #74 ultra-blue filter replaces the infrared blocking filter in the back of the lens holder.
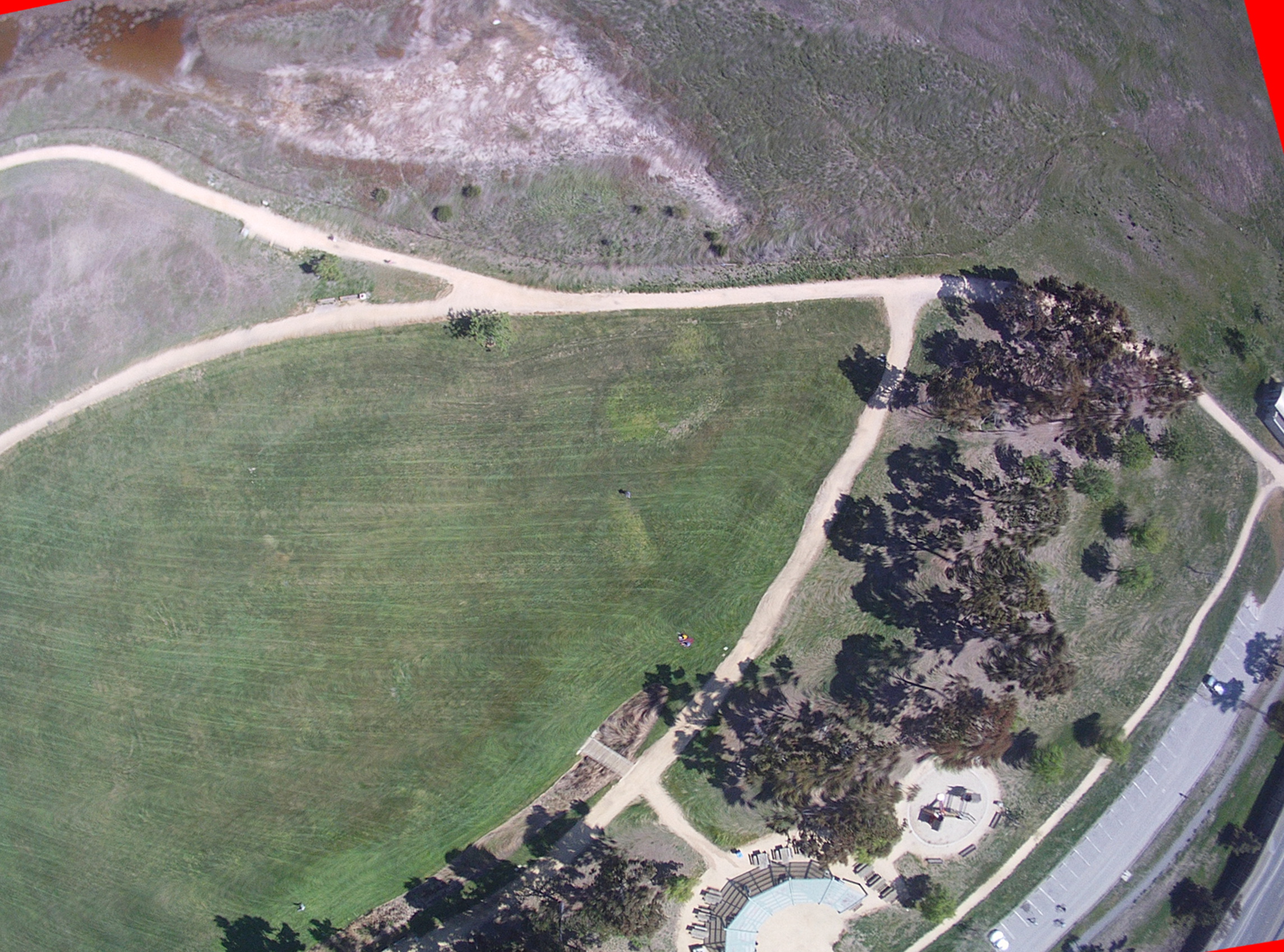
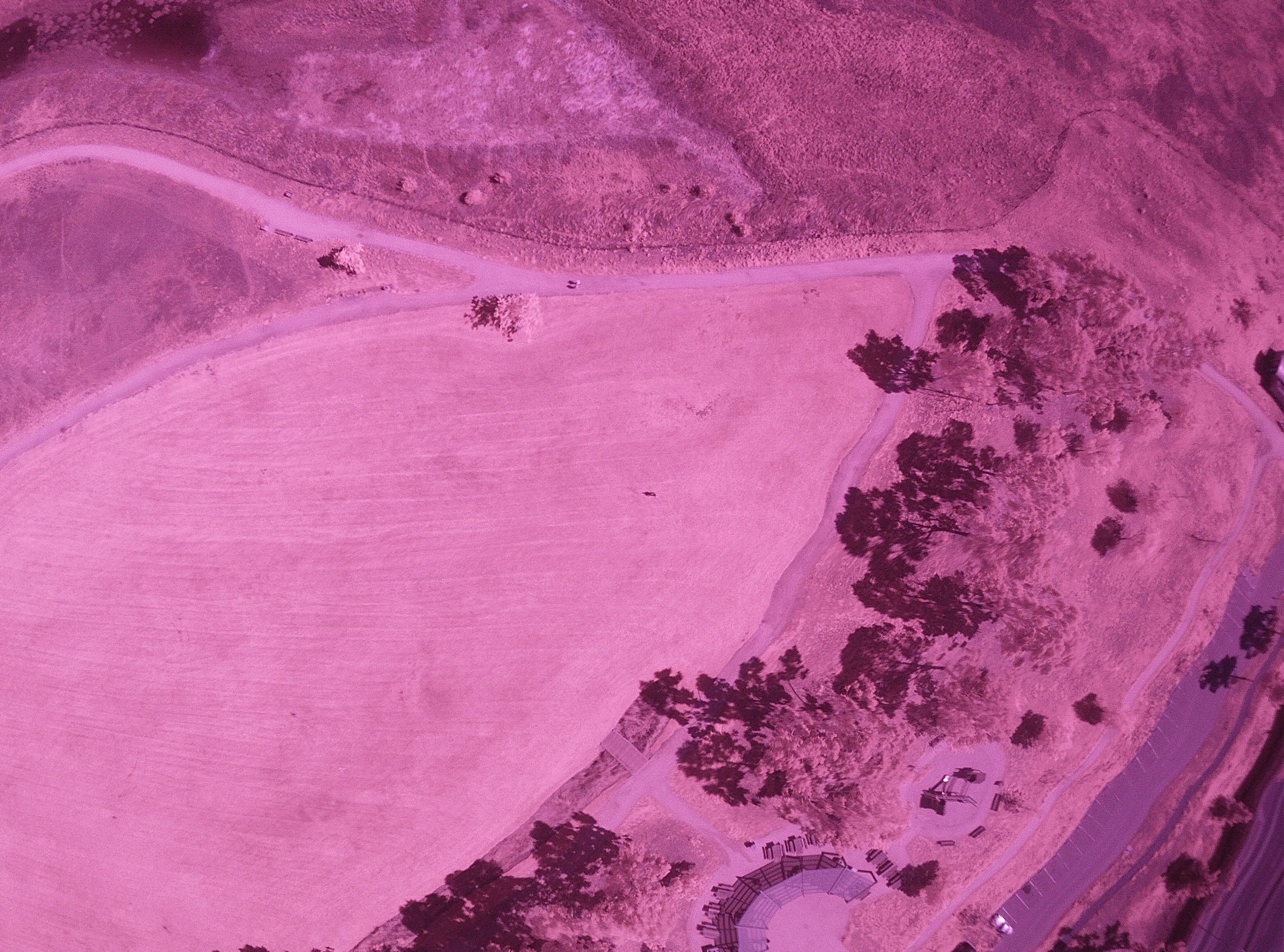
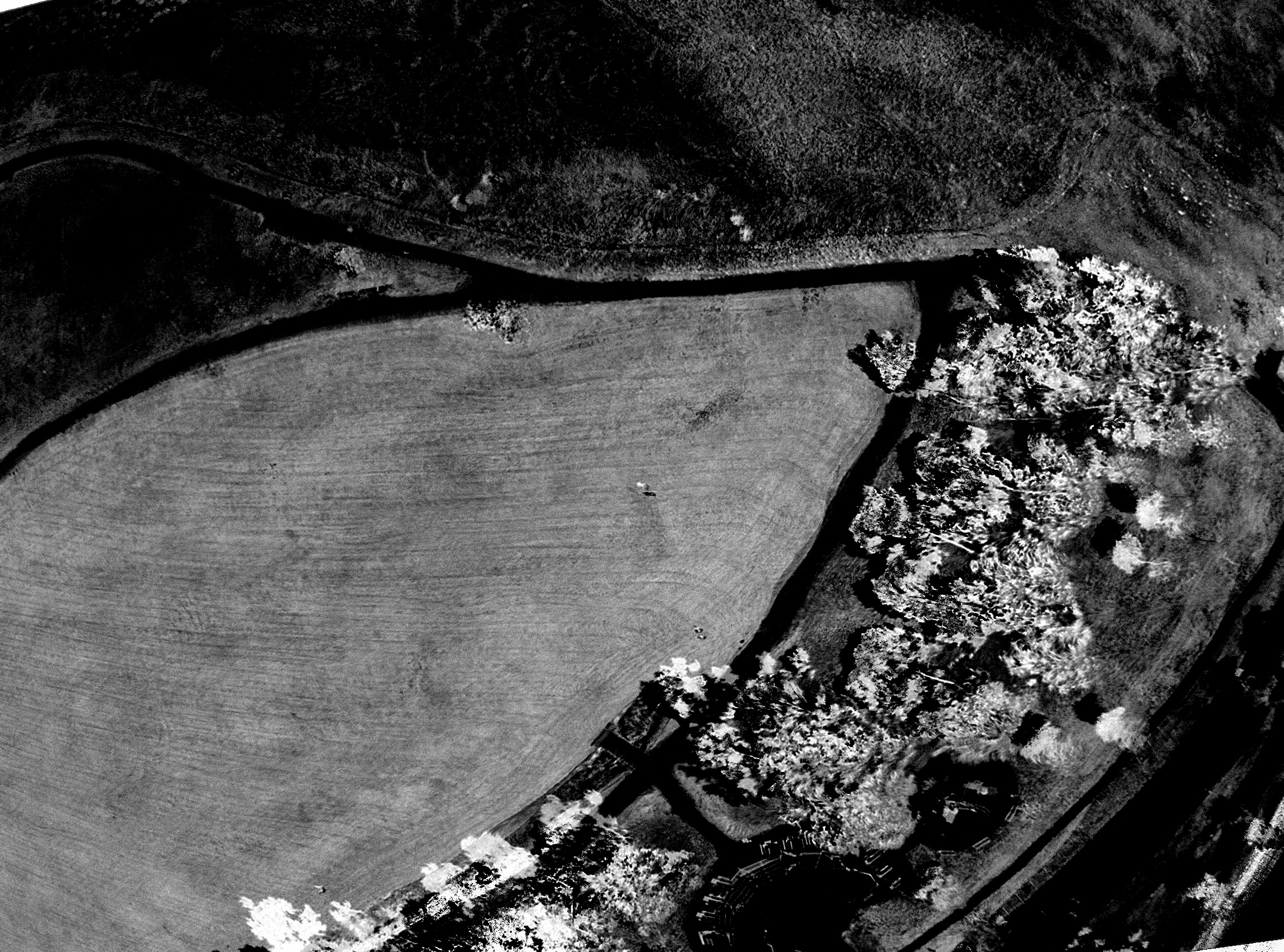
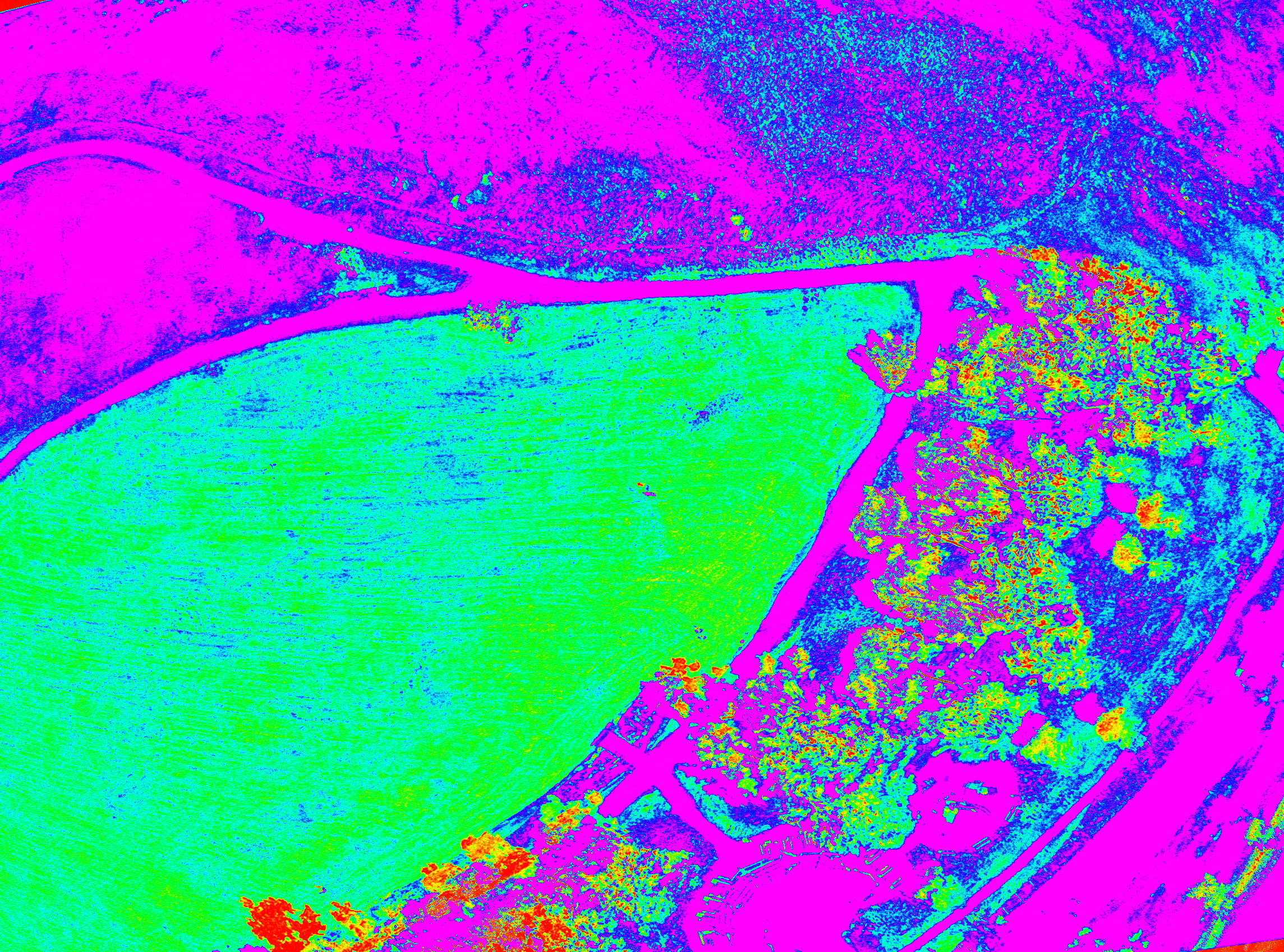
Below is a series of four images showing a standard RGB photograph, followed by a NIR (near infrared image) composite into a grey scale NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index). This shows the reflected infrared light that a healthy plant will reflect during photosynthesis. The final image is known as a false heat map and is designed to enhance a grey scale NDVI to show more clearly areas where the plant health is compromised due to pests, disease, lack of water or proper fertilizer.